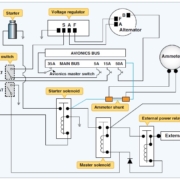
Electrical System Components
Electrical System Components
Electrical systems are composed of a variety of different components that must work together for the system to function properly. These components include circuit breakers, transformers, power converters, relays, and other electrical equipment. In order for the system to be efficient and reliable, these components must be selected appropriately in order to meet the requirements of the application. Furthermore, they must be integrated properly in order for the system to perform optimally. In this article, we will discuss some of the key components that make up an electrical system and how they interact with one another. . Circuit Breakers. A circuit breaker is a critical component of an electrical system. It is used to protect the equipment and people in case of an overload that overpowers the system. It also allows devices to be turned on or off in case they are connected with a switch. Some circuit breakers, such as combination circuit breakers, can serve multiple purposes simultaneously. In most cases, circuit breakers are installed on circuits that have been sized for the loads they are expected to carry and maintain desired safety factors while carrying them. Furthermore, they can be adjusted by employing different operating modes and settings. These settings can be made manually by adjusting the position of the circuit breaker, or automatically. For example, a circuit breaker that is designed to be adjusted automatically can change its settings if it detects a particular load on the circuit. Circuit breakers are usually installed together with fuses in distribution boards and panels and are connected in series with them to reduce short circuits, overcurrent and flames caused by overloaded circuits. They can be installed remotely from terminals (the plug-in type) or on-board (the main type).The first use of a fuse was in 1753 when William Sloan invented an attachment for the chimney of a fireplace that used a glass tube filled with mercury as an insulator and a steel wire coiled around it. The short-circuited wire would bridge the broken end of the glass tube and when a spark ignited the mercury, then people could extinguish the fire more quickly. A fuse is an electrical device that provides complete or partial protection against electric current overloads by interrupting power in designated protected circuits. Generally, this interruption is characterized by melting its terminals to interrupt conducting current flow at higher currents. In some cases, fuse clips can protect circuits from overloads or arc faults by interrupting power at lower currents. Fuses cannot be used to protect circuits from short circuits, which may cause the fuse to blow, but they can protect circuits from overloads caused by insulation failures (such as a short circuit).