Current
What is electric current –
Definition of electric current is given below –
Definition – Electric Current is the rate at which charge flows. It is measured in Amperes (A). It is denoted by letter I. Voltage is the driving force for current to flow in the circuit. Current flows from higher potential to lower potential.
(Note:-When we say current flows in a circuit, electrons flow from lower/negative potential to higher potential while the direction of current is kept from higher to lower/negative potential.)
Types of electric current–
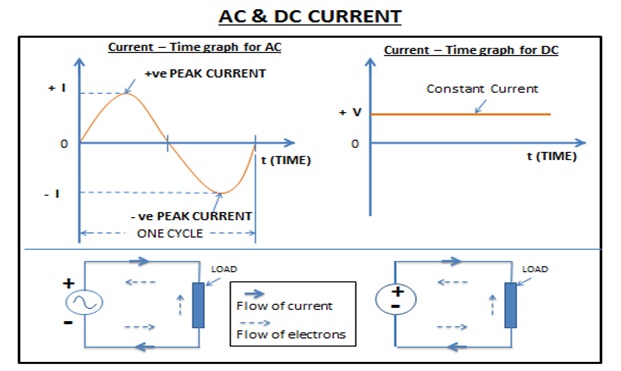
There are two types of electric current – AC current & DC current.
AC (Alternating Current) –
It varies with respect to time and forms sinusoidal waves. Same as ac voltage it periodically reverses its direction. AC current flows in the circuit when AC voltage is applied to it.
DC (Direct Current) –
DC current doesn’t vary with time so it is represented by a straight line. DC current flows in the circuit when DC voltage is applied to it.
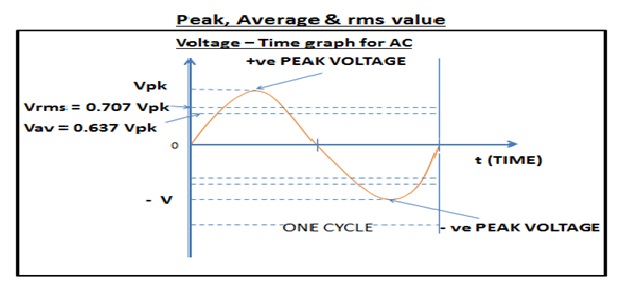
RMS value, Peak value & Average value –
There are some terms associated with AC Voltage & Current which we must understand like RMS value, Peak value & Average value.
Peak Value of Voltage & Current –
It is the maximum value of voltage/current. Peak value is positive in first half of cycle & negative in another half cycle. In other words, in a complete cycle, voltage/current with respect to time varies from zero value to peak (+ve) value then again becomes zero & then goes to (-ve) peak value & then again it becomes zero value& this cycle is repeated.
Average value of Voltage & Current –
Average value of a voltage for one complete cycle is 0 as two half values (one positive & one negative) cancels each other out. Hence average value is taken from half cycle whose value is 0.637 times the peak value of voltage.
Vav = 2/π X Vpk = 0.637 Vpeak
Similarly, Average value of Current Iav= 0.637Vpeak
Rms value of Voltage & Current –
RMS (Root Mean Square) value of voltage & current is the average effect in ac circuit. Only RMS value is used for measuring & calculation purpose. Rms value of AC voltage & Current is equivalent to DC value that would produce the same output voltage.The RMS value of voltage (or current) is 0.707 times of peak voltage and 1.11 times of average value.
(Note –Multi-meters & other AC meters (voltage & current) giverms value of voltage & current.)
Vrms= 0.707Vpeak = 1.11Vav,
Irms = 0.707Vpeak = 1.11Iav
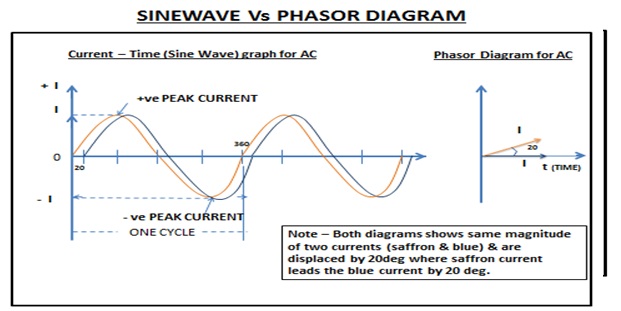
PHASOR DIAGRAM (VECTOR DIAGRAM) –
AC voltage & Current can also be analyzed by phasor diagram when frequencies are same but amplitude need not be same. Diagram given below shows a sine wave represented by phasor.
In above diagram, two voltages have the same amplitude; therefore the length of arrow of both voltages is same. The saffron current leads the blue current by 20 deg.
Formula of Electric Current –
Current in a circuit can be calculated with the help of Ohm’s law which says that voltage across the load is directly proportional to the current.
So, we can write, V α I (where V= Voltage across load & I is current), or
V = R I (where R is a constant & its value depends on the material/load through which current flows. R is also known as Resistance).
Or Current, I = V/R
Therefore, we can say that current’s value depends on voltage & resistance. If voltage across the load is constant than current value will vary according to resistance value. If resistance value is low, then current value will be high & vice versa.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Current –
Q1) What are the effects of electric current?
Ans) There are 3 main effects of electric current – a) Magnetic effect, b) Heating effects, c) Chemical effect.
With the help of above effects, electric current is widely used in our day to day life & that is not limited to domestic purpose but also for commercial & industrial purpose also.
Q2) What is magnetic effect of electric current?
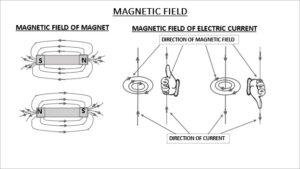
Ans) When electric current passes through a wire, it produces magnetic effect or magnetic field around it. The magnetic field is produced in a particular direction.
Magnetic field by normal magnet–
First let’s understand that how a normal magnet behaves. We all know that a magnet has two opposite poles- North & South. Each magnet has some effect around it & this effect we can call it ‘magnetic field’. This magnetic field is represented by imaginary lines which originates from North pole, travel outside the magnet & conclude to South pole. Or in other words we can say that the direction of magnetic field is from N-pole to S-pole. This magnetic field is strong near the poles & its strength reduces gradually when go away from the magnet. This can be understood from the diagram given below.
Magnetic field by electric current –
The magnetic effect from electric current discovered by the Hans Christian Oersted in April, 1820 when he observed that the needle of compass which was kept near the current carrying wire deflected.
This can be understood by Maxwell’s right hand thumb rule which says that when a current flows in a conductor, a magnetic field is produced around it. If current flows upwards, magnetic-filed will be produced in anti-clock wise direction & if current flows downwards then magnetic-filed direction will be clock wise. This has been explained in the diagram below.
In other words, electromagnetic can be defined as a magnet which works on electric current.
Difference between permanent magnet & electromagnet –
- Strength of permanent magnet is constant while strength of electromagnet depends on the value of current.
- The strength of magnetic field is constant in permanent magnet while strength of magnetic field varies with the strength of electromagnet.
- Poles in permanent magnet is fixed while it can be revered in case of electromagnet.
Usage / Applications of electromagnet –
The electromagnetic effect is widely used in our daily life. Following are some major examples given below-
- Electric motors,
- Electric generators,
- Transformers,
- Induction heating,
- MRI machines,
- Amplifiers/Loud Speakers,
- Telephones
Q3) Heating effect of electric current?
Ans) In heating effect when electric current passes through a material, heat is generated. A high resistive materail such as nichrome wire (alloy of Nickel & Chromium in 80:20 ratio) is used for heating purpose.
Application of heating effect of electric current –
This heating effect is used in many daily equipment such as Incandescent bulb, heater, iron, toaster, electric kettle & some cooking devices also.
Q4) Chemical effect of electric current?
Ans) Let’s understand first chemical reaction, chemical reaction takes place in a liquid (conducting solution) when current passes through it.
Conducting solution is a liquid (a solvent when water is used) in which ionic solid substance (known as solute) is dissolved, ions of solid substance got separated, become free & move freely in the liquid. These ions are mobile, carry different charges in the solution & become conductive solution. (Note- Solute & solvent don’t have free ions while solution has free & mobile ions.)
This can be understood by this example- When salt (NaCl) is dissolved in water, it breaks down into Sodium (Na+) ion & Chloride (Cl-) ion & makes liquid conducting solution as these positive & negative ions move freely in the solution. These free mobile ions are responsible for conducting electricity.
Types of Liquids which conduct electricity –
Not all liquids are good conductors of electricity, some are good & some are bad conductors.
Good conductors – Normal water is not a good conductor, but when some material (which have positive & negative ions) like such as salt or other minerals such as Lemon Juice, Mercury, Soda compound etc are dissolved in it, the solution becomes good conductor.
Bad conductors – Other material like Vinegar & honey are dissolved in water, the solution becomes bad conductor.
Effects of electricity when passes through conducting solution –
When electric current passes through the conducting solution, chemical reaction takes place & current flows in the solution. During chemical reaction, gas bubbles originate, start moving & depositing on the electrodes. These deposits (positive & negative ions) could be seen on electrodes & the colour of the solution may change. Also, movement of ions in the solution causes flow of current the solution.
Usage of chemical effects of electric current –
Following are the usage or application of chemical effects of electric current –
- Electroplating
- Extracting metals from their ores
- Purification of metals,
- Production of compound
- Decomposition of compounds
Q5) What is SI unit if electric current?
Ans) The SI unit of current is Ampere. In the International System of unit, Ampere is denoted by A. The name Ampere is given after the name of a French scientist Andre-Marie-Amperein.
Q6) Instrument which detects electric current is known as?
The instrument that detects /measures electric current is called Ammeter (short form of Ampere Meter). The current is measured in Amp or A.
Q7) Who invented electric current?
Ans) Electric current is nothing but conduction of electricity. But the rate at which charge flows (electrons from higher potential to lower potential) in a circuit is called electric current. The credit of electricity invention is given Benjamin Franklin.
