Why Lithium-ion batteries are used in electric vehicle (EV)?
Why Lithium-ion batteries are used in electric vehicle

Battery For Electric Vehicle
As we know that the performance of an EV depends on the coverage of distance by the vehicle in single charge. Therefore, rechargeable batteries are used in EVs so that after discharge of batteries they can be charged again. These days there is no good infrastructure (charging stations) available in countries hence the success of EV totally depending on the type of battery which could provide power to a vehicle for a long period so that EV can cover more distance. The function of charging stations is like petrol pumps for engine/fuel vehicle.
(Note – A battery bank in EV works as a source of power like fuel (such as diesel, petrol etc in the tank) works for internal combustion engine vehicle.)
Various types of batteries are used for various purpose such as Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, Lead Acid batteries, Nickel-Metal Hydrite batteries etc. But Lithium-ion batterie are used in EVs because of higher energy density or high power to weight ratio as compared to other batteries. That is why Li-ion batteries are also used in mobile phones, laptops etc.
Advantages of lithium-ion batteries over other batteries are given below –
- Higher energy density or high power to weight ratio,
- High energy efficiency
- Excellent good-temperature performance
- Low self-discharge rate
- No problem in charging of fully discharged battery
- Long life of battery. As such there is no concrete evidence to claim the life of Li-on batteries but it is predicted that the life of battery will vary from 5-10 years but some also claim that it may go up to 15 years or more (depending on the usage of vehicle.
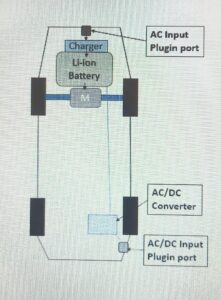
BATTERY BANK IN ONE OF THE VEHICLES (FRONT SIDE)