Electricity
What is electricity –
Electricity is a form of energy which is generated by flow of charges such as electrons (a negative charged particle) which are present in the material (solid & liquid). Flow of charge is possible in conducting material through electrostatic force, in the liquid through chemical reaction (ex.- battery), in semiconducting material through solar energy.
Charge & Atoms –
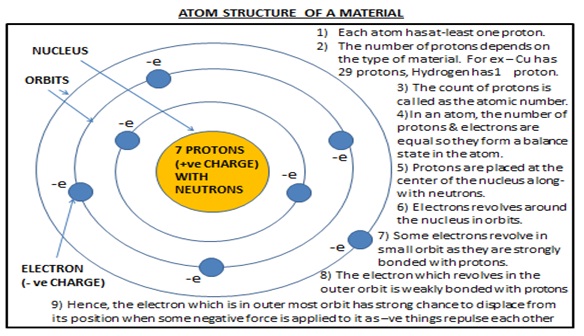
Let’s understand the charges in a material. As we know that a material is made up of small – small atoms, each atom consists of three particles- proton, electron & neutron. Protons are positively charged particles, electrons are negatively charged particle & neutron carries no charge so it’s a neutral particle. These positive & negative charges are equal in numbers & attract to each other hence a balanced condition is formed in the atom.
An atom has a center point called nucleolus where protons are present at the center along with neutrons & electrons are placed in orbits surrounding the nucleus. Some orbits are smaller which are very close to center & other orbits are at a regular distance from the center.The electron which is revolving close to nucleus is strongly bonded with the protons & the outer most is weakly bonded with the protons. The attraction force between protons & electrons depends on the distance between them. These attraction & repulsion forces are called electrostatic forces. Each material has fixed number of electrons in the orbit & the electrons in the outmost orbit are called valence electrons which can move when a negative external force is applied to it.
Static Electricity –
These atoms are attached with each other as outer most electrons repulse to other electron of other atom which is further pushed towards protons. Like this, these atoms are joined together, form molecules & then substance & becomes a material.
Some examples of static electricity /charge flow –
- Comb gets charged when combing our dry hair. During combing process, electrons (loosely connected with hair) move from hair &attach with comb, now comb becomes negative charged object& hair positively charged. That is why our hair stands up when we bring comb close to hair.
- When we bring small piece of paper close to charged comb, paper is attracted towards comb because paper is not charged & a charged particles (like comb) may attract or repulse a without charge material according to other material’s neutral property. Hence in case of paper & comb, paper is attracted towards negatively charged comb.
- Such type of charge flow is called static electricity.
HOW DOES CHARGEFLOW IN A MATERIAL –
As we have seen that outer most electron or valence electron can be separated from the atom if a suitable electrostatic force is applied to the atom. Now the separated electron is a free electron.
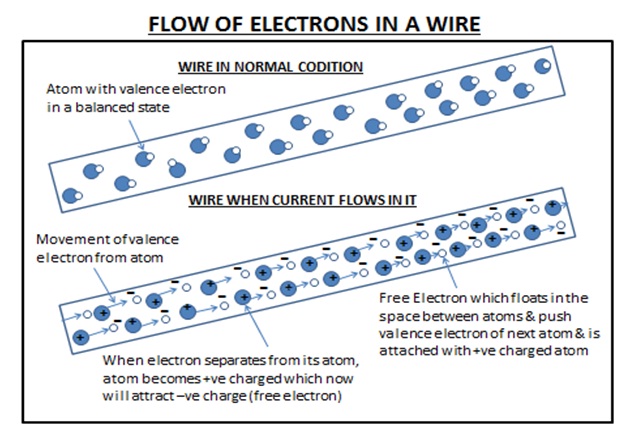
Let us consider a case of wire which is made up of a conducting material. Now this wire is filled with countless atoms in it. When an electrostatic force is applied in the wire, valence electron separates from the atom & floats in the space between the atoms, this free –ve charged electron push another electron of outer orbit of next atom & takes its position, now this free electron floats in the space & it does same & this process repeats. So, the chain of flow of electrons in the wire is called electric current.
The flow of electrons depends on the type of material which requires less force to separate valence electron. There is some material known as conducting material which needs less force to separate valence electrons such as Cupper, Aluminum etc. On the other hand there is some material which needs high force to separate free electron from atoms such material is called insulators like rubber, plastic etc.The same could be understood with the diagram given below.
WHAT IS ELECTROSTATIC FORCE –
Electrostatic force which is also kwon as Coulomb force, is the attraction or repulsion of particles or objects because of their electric charge.
Two like electric charges, both either positive or negative repel each other in a center line between their centers. Two unlike charges, one positive & one negative attract each other along a straight line joining their centers.
When we talk of electricity, we come across few terms like Voltage, Current, Resistance, frequency etc , which have been explained in next lessons.
Electricity is a form of energy which is generated by flow of charges (ex.- positive charge, negative charge) which are present in the material (solid & liquid). Flow of charge is possible in conducting material through electrostatic force, in the liquid through chemical reaction (ex.- battery), in semiconducting material through solar energy.
Let’s understand the charges in a material. As we know that a material is made up of small – small atoms, each atom consists of three particles- proton, electron & neutron. Protons are positively charged particles, electrons are negatively charged particle & neutron carries no charge so it’s a neutral particle. These positive & negative charges are equal in numbers & attract to each other hence a balanced condition is formed in the atom.
An atom has a center point called nucleolus where protons are present at the center along with neutrons & electrons are placed in orbits surrounding the nucleus. Some orbits are smaller which are very close to center & other orbits are at a regular distance from the center. The electron which is revolving close to nucleus is strongly bonded with the protons & the outer most is weakly bonded with the protons. The attraction force between protons & electrons depends on the distance between them. These attraction & repulsion forces are called electrostatic forces. Each material has fixed number of electrons in the orbit & the electrons in the outmost orbit are called valence electrons which can move when a negative external force is applied to it.
These atoms are attached with each other as outer most electrons repulse to other electron of other atom which is further pushed towards protons. Like this, these atoms are joined together, form molecules & then substance & becomes a material.
Some examples of charge flow –
- Comb gets charged when combing our dry hair. During combing process, electrons (loosely connected with hair) move from hair &attach with comb, now comb becomes negative charged object& hair positively charged. That is why our hair stands up when we bring comb close to hair.
- When we bring small piece of paper close to charged comb, paper is attracted towards comb because paper is not charged & a charged particles (like comb) may attract or repulse a without charge material according to other material’s neutral property. Hence in case of paper & comb, paper is attracted towards negatively charged comb.
- Such type of charge flow is called static electricity.
HOW DOES CHARGEFLOW IN A MATERIAL –
As we have seen that outer most electron or valence electron can be separated from the atom if a suitable electrostatic force is applied to the atom. Now the separated electron is a free electron.
Let us consider a case of wire which is made up of a conducting material. Now this wire is filled with countless atoms in it. When an electrostatic force is applied in the wire, valence electron separates from the atom & floats in the space between the atoms, this free –ve charged electron push another electron of outer orbit of next atom & takes its position, now this free electron floats in the space & it does same & this process repeats. So, the chain of flow of electrons in the wire is called electric current.
The flow of electrons depends on the type of material which requires less force to separate valence electron. There is some material known as conducting material which needs less force to separate valence electrons such as Cupper, Aluminum etc. On the other hand there is some material which needs high force to separate free electron from atoms such material is called insulators like rubber, plastic etc. The same could be understood with the diagram given below.
WHAT IS ELECTROSTATIC FORCE –
Electrostatic force which is also kwon as Coulomb force, is the attraction or repulsion of particles or objects because of their electric charge.
Two like electric charges, both either positive or negative repel each other in a center line between their centers. Two unlike charges, one positive & one negative attract each other along a straight line joining their centers.
When we talk of electricity, we come across few terms like Voltage, Current, Resistance, frequency etc , which have been explained in next lessons.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Electricity –
Q1) When electricity was invented? Who invented the electricity? Who created electricity? When was electricity discovered?
Ans) Electricity already exists in the nature since beginning. But credit of discovering electricity is given to Scientist Benjamin Franklin. He found it during an experiment in 1752 through a kite experiment. The term electricity has come from Greek word Amber. Scientists have been working on different aspects of electricity for last many years, some examples are given below –
· In 600 BC, Greeks noticed electricity by rubbing fur on amber in 600BC.
· In 1600, Physician William Gilbert explained force between material when they are rubbed with other & used word “electricus” for the first time.
· In 1831, Michael Faraday invented electric dynamo
· In 1879, electric bulb with carbonized filament was invented by the Thomas Edison
· In 1883, Thomas Edison invented electric heater
· In 1868, Englishman Benjamin Maughan invented water heater called “Geyser”
· In 1885, Nikola Tesla invented first AC polyphase induction motor
· In 1889, A Norwegian engineer Edwin Rudd invented electric water heater.
Q2) What causes static electricity?
Ans) When positive & negative charges become imbalance (or charge flows) in an object, static electricity is produced. In this process, charges build up the surface of the object & gets discharged when another object comes close to it. This happens when certain materials rub with each other. This can be understood by following example – during dry winter, when you remove hat from your head, hair rises.
Q3) How to get rid of static electricity? How to remove static electricity from body?
Ans) Static electricity phenomena occur mostly in dry winter when some material like hair & some fabrics release electrons easily when they are rubbed or experience friction then we come across following things –
1) Hair stands up when hat is taken off from head,
2) Hair stands up when we comb dry hair,
3) Chattering & sparking are observed when we use blanket,
4) We get a shock when we touch the metal door of the car after some driving & woolen cloths are worn by us,
5) A small shock/spark is experienced when we hand over the key to someone after some driving & woolen cloths are worn by us,
Now, how to get rid of above situations. Do following things –
Hair standing up issue could be resolved by using some water on hair or moist the hair. Or wait for some time, the static electricity will dissipate naturally in few minutes.
To avoid chattering/sparking in the blanket, we should increase the humidity level in the room.
To get rid of body charge after driving a car, discharge your body by touching metallic/conductive material which should not be isolated from the ground such as a screw on a light panel etc.
Q4) Where does electricity come from? Or How is electricity generated or made?
Ans) Electricity is a natural phenomenon which can be experience from flow of charge in some material such as hair stand up when we comb or take off hat or flow of electricity/current through lightening during thunderstorm etc. If we talk about electricity for daily use for domestic or commercial purpose, it comes from power generating plants.
These power generating plants may be thermal power plant where coal is used for electricity, hydro power plant where water from dams is used to generate electricity, atomic power plants where nucleus fission/fusion is used for electricity generation, Solar power plants where sun ray are used to generate electricity.
Apart from above major power plants, there some small capacity power plants are also available such as Diesel Generator sets, PNG gas based power plants, waste to energy power plants, power from biomass etc.
Q5) Who invented electricity bulb?
Ans) Thomas Edison has invented electricity bulb. He practically developed incandescent bulb in 1878 & filed his patent on “improvement in electric lights” on 14th Oct, 1878. But he continued his experiment on this product where focus was on filament to improve the performance of bulb & finally Thomas Edison & his team discovered that carbonized bamboo filament could be used for 1200 hrs. Then in 1880, they started promoting its product for commercial use.
Q6) How fast does electricity travel?
Ans) There are different answers on the speed of the electricity. Electricity & light both are electromagnetic radiations. The EMR (electromagnetic radiations) consists of waves that propagates through the space & carry electromagnetic energy. EMR is a type of energy that is all around us which includes radio waves, microwaves, X-rays and gamma-rays. Sunlight is also a form of electromagnetic energy. In a vacuum, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of the light. Therefore, we can say that electricity travels at the speed of the light & its value is 2.99 x 108 m/s or 60,616,629 miles/hour or 186,282 miles/sec.
Q7) How do eels produce electricity?
Ans) The body of Eels works like a battery where its head acts as a positive pole & tail is a negative pole. The entire body (like cells in a battery) contains hundreds of thousands of modified muscle cells called electrocytes. These cells get activated when eel senses danger or sees prey, it sends signal through its nervous system to the electrocytes. The nerve fiber connects electrocytes at one end & on signal arrival, positively charged sodium ions to flood into the cell.
This process produces potential difference across the cell. The voltage produce from each cell is very small i.e. aprox. 150mV, but each electrocyte is placed in series & parallel like cells in battery where series placement increases voltage & parallel increases current.
Therefore, when eel gives signal, all these electrocytes work together & produce high voltage up to 500V & with a current value up to 1A.
Most electric fish produce AC current (pulse type) signals. An eel can produce weak & powerful electric signals by using combinations of electrocytes.
Q8) How electricity works?
Ans) Electricity is produced when flow of electric charges (protons and electrons) take place in an object. The rate at which negative charge (electrons) flows is called current. In other words, we can say that when current flows in a material, electricity is produced, or conduction of electricity takes place.
Currents always flows from higher potential to lower potential in a closed circuit. The level of potential is produced when electrons leave the place. Potential will be higher at a point when more negatively charged particles (electrons) will be separated & the location where these electrons will be accumulated will become low potential point.
For practical purpose, many sources of electricity have been developed through which we can get electricity or electrical power such as thermal generators, hydro power plants, batteries, solar power plants etc.
Q9) How does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
Ans) As we know that conduction of electricity in liquid depends on the ions present in it. Therefore, in aqueous solution of an acid, ions are responsible for conduction of electricity because acid dissociates to produce ions.
What is aqueous solution – It is a solution that has water as a solvent. In chemistry, it is represented by appending (aq). For example – Table salt (NaCl), when salt is mixed with water (solvent), it is represented by Na+ (aq) + Cl – (aq) ions where Na represents Sodium, Cl represents chloride & NaCl is Sodium Chloride.
Let’s take another example of Hydrochloride Acid (HCL). It give H+ (aq) and CL + (aq) ions & these ions in aqueous solution of acid conducts electricity or carry electric current. H represents Hydrogen & CL represents chloride.
Q10) Why does distill water not conduct electricity whereas rainwater does?
Ans) Conduction of electricity in water depends on ions which are present in dissolved salt/ solute in it. Distill water is a pure form of water which does not contain any dissolved salt therefore, distill water doesn’t conduct electricity because it doesn’t have ions in it while rainwater conduct electricity because salt dissociates in ions.
Q11) In terms of electricity what does AC stand for?
Ans) AC stands for Alternating Current. There are two forms of electricity – AC & DC where DC stands for Direct Current. In AC form, the value of voltage & current varies with respect to time. First, from zero it goes up to its peak value positive side then comes back to zero & then goes peak negative side. This cycle repeats again & again. The power which comes to our house from grid is AC power & all the equipment which we use, are designed for AC power or supply only.
While in DC, the value of current remains constant at its peak value with respect to time.
Q12) Examples of good & bad conductors for electricity?
Ans) Good conductors – For practical usage purpose, Copper is considered the best conductors for electricity. Then comes the name of Aluminum.
Bad conductors – Rubber, plastic, wood etc are examples of bad conductors for electricity.
Q13) How does a Firefly (Jugnoo) glow?
Ans) A firefly (or Jugnoo) is an insect that glows at night. Fireflies are mostly seen in summer nights because they flourish in warm & humid/steamy areas. This is very special phenomenon in a living being. The process of producing light is called Bioluminescence. This is a chemical reaction that takes place in the stomach of the firefly when air (oxygen) rushes to the abdomens, it reacts with the luciferin (which is a organic compound of the firefly) & produce light. This light is also called cold light also because this process generates very little heat.
