SWITCHGEAR ITEMS
SWITCHGEAR –
The apparatus used for switching, controlling and protecting the electrical circuits and equipment is known as switchgear.
The term ‘switchgear’ is a generic term which includes a wide range of products like circuit breakers, switches, switch fuse units, off-load isolators, HRC fuses, contactors, earth leakage circuit breakers (ELCBs), etc…
CIRCUIT BREAKERS
What is Circuit Breaker –
Definition of circuit breaker is given below –
Definition –A Circuit Breaker is a piece of electrical equipment/device which can make or break a circuit either manually, remotely or automatically under all conditions like no load, full load & short circuit.
WORKING PRINCIPLE OF ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT BREAKER–
It consists of fixed & moving contacts (or electrodes), the moving contacts are connected with a coil called trip coil. Under normal operating conditions, these contacts remain closed. When a fault occurs on any part of electrical system, the trip coil of the breaker gets energized & moving contacts are pulled apart by some mechanism thus opening the circuit.
When the contacts of a circuit breaker are separated under fault conditions, an arc is struck between them due to which current is able to continue until the discharge ceases. The production of arc not only delays the current interruption process but it generates enormous heat which may cause to damage the system or breaker itself. So, arc should be extinguished within the shortest possible time in order to protect the system or breaker from damage.
Arc–
When a short occurs in the circuit, heavy current flows through the circuit breaker before contacts are separated. When contacts begin to separate, the contact area (between fixed & moving contacts) decreases rapidly & density of fault current increases which causes increase in temperature between contacts. The area between contacts is either air or oil. The high temperature is sufficient to ionize the air or vaporize and ionize the oil. The ionized air or vapour acts as conductor & arc is struck between contacts. The potential difference (p.d) between the contacts is quite small but sufficient to maintain the arc.
In other words we can say that p.d and ionized particle are responsible to maintain the arc between the contacts. The arc provides a low resistance path & current remains in the circuit uninterrupted as long as arc persists.
Methods of arc extinction–
There are two methods of extinguishing the arc –
- High Resistance method,
- Low resistance method.
High Resistance method –
In this method, an arc resistance is made to increase with time so that current is reduced to a value insufficient to maintain the arc. As enormous heat is generated so this method is used for DC circuit breakers & low capacity AC circuit breakers.
Low resistance method –
In this method, arc resistance is kept low until current zero where arc extinguishes naturally and is prevented from re-striking in-spite of the rising voltage across the contacts. This method is used for all modern high powers breakers for arc extinction.
TYPES OF ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT BREAKERS –
According to voltage, circuit breakers can be classified into HT & LT Circuit breakers.
- Types of HT Circuit Breakers – There are several ways of classifying HT CBs (circuit breakers) but according to medium of fire extinguishers, circuit breakers are classified into –
- Oil Circuit Breakers,
- Air blast Circuit Breakers,
- Sulphur Hexa Fluoride (SF6) Circuit Breakers,
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers,
(Note – HT circuit breakers are used for 11KV, 33KV,..etc electrical system.)
- OIL CIRCUIT BREAKER – In such breakers, some insulating oil (e.g. Transformer oil) is used as an arc quenching medium. The contacts are opened in the oil & an arc is struck between them. The heat of the arc is evaporates the surrounding oil & hydrogen gas is produced. So, the arc extinction is done by two process –
- Hydrogen gas has high heat conductivity & cools the arc thus adding de-ionization of the medium between contacts,
- Gas sets up the turbulence in the oil & forced it into the space between contacts thus eliminating the arcing products from the arc path. Thus, the arc is extinguished & circuit current is interrupted.
Types of oil type circuit breaker –
- Bulk oil circuit breakers,
- Low oil circuit breakers,
- AIR BLAST CIRCUIT BREAKER –In this method, arc is quenched under a high air blast. The contacts are opened in a flow of air blast established by opening of last valve. The air blast cools the arc & sweeps away the arcing products to the atmosphere. And arc is extinguished & flow of current is interrupted.
Types of Air Blast type circuit breaker –
- Axial blast type circuit breakers,
- Cross blast type circuit breakers,
- Radial blast type circuit breakers,
- SF6 (SULFURIC HEXA FLUORIDE) CIRCUIT BREAKER – In this method, SF6 gas is used as the arc quenching medium. The SF6 is an electro-negative gas & has a strong tendency to absorb free electrons.Also it has high dielectric strength, good heat transfer properties which are suitable for breaker operations.
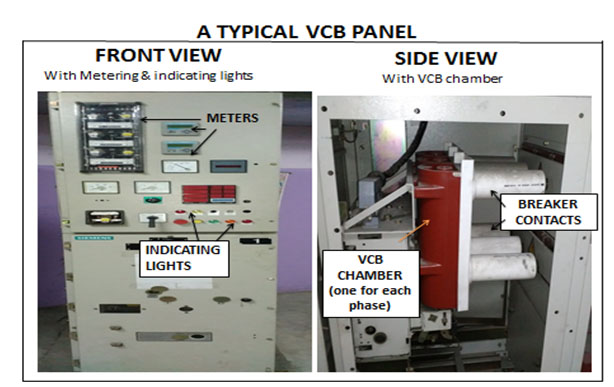
- VACUUM CIRCUIT BREAKER – In this method, vacuum is used as the arc quenching medium. Since vacuum offers highest insulating strength, it has far superior arc quenching properties than any other medium. When contacts are opened in vacuum, the interruption occurs at first current zero with dielectric strength between the contacts building up at a rate thousands of times higher than that obtained with other circuit breakers.
(Note: Vacuum is a space which is devoid of matteror without air or any other substance/matter.)
Circuit Breaker Ratings –
The circuit breakers have 4 ratings –a) Breaking Capacity, b) Making Capacity, c) Short time rating & d) Normal current rating.
- Breaking Capacity – It is the R. M.S value of the current that a circuit breaker is capable of breaking. Breaking capacity of a breaker is required when a fault occurs in the system & contacts are separated.
Breaking capacity is expressed in MVA & it is measured by following formula –
Breaking Capacity = Г3 X V X I X 10-6MVA
Where V= Rated service line current, I = Rated breaking current
It’s a common practice to take breaking current equal to symmetrical breaking current.
- Making Capacity – It is the peak value of the current during the first cycle of current wave after closure of electrical breaker is known as making Capacity.
In other words, the making capacity is equal to the maximum value of asymmetrical current.
Breaking capacity is measured by following formula –
Making Capacity = 2.55 x Symmetrical breaking capacity
- Short-time rating – It is the period for which the circuit breaker is able to carry fault current while remaining closed. It is very important rating when a fault occurs in the system for few seconds & cleared automatically. In this situation the circuit breaker should be capable to carry fault current. But if fault current persists for a longer period than the specified period then breaker will trip & faulty section will be disconnected.
- Normal current rating – It is the r.ms. value of the current that the circuit breaker is capable to carry continuously under specified conditions.
Important points to note –
- Closing of breaker – It means switching on the breaker. It’s a process by which breaker changes its position from off to on. It can be done either manually or electrically. Closing of breaker is done with help of a spring which needs charging (spring tension /mechanical charging) before changing its position. This spring can be charged manually or electrically.
- Manual Closing – In manual closing, spring is charged with the help of a rod & we press it repeatedly (up & down). Spring gets charged & breaker is ready to change position. To switch on breaker, press red color button (ON button) to close. When breaker gets on, spring gets discharged& again needs charging for next operation.
- Electrical closing – A single phase ac motor is installed in the breaker to get the spring charged. Electrical supply is connected with a limit switch. When spring is charged electrical supply is disconnected automatically. Breaker can be switched on either by pressing red push button (manually) or through a TNC switch. Electrical closing of breaker is done by a coil called closing coil.
- TNC Switch – TNC stands for Trip, Neutral & Close. TNC switch is used to close or trip the breaker electrically. Neutral is the position where switch remains neutral. We rotate it left to trip the breaker & right to close it.
- Tripping of breaker – When breaker changes its position from ON to Off, it is called tripping of breaker. This can be done manually by pressing green button in the breaker or electrically by twisting TNC switch or automatically on fault or remotely through a distanced command. Tripping operation is carried out with help of a coil that is called tripping coil.
Tripping of breaker on fault – Tripping of breaker is required when a fault occurs in the system. Different types of faultsoccur in the circuit which needs to be detected & isolated to protect the equipment & interruption of service to the consumers. Fault detection is done by different types of relays. After sensing the fault, relay gives tripping command to the trip coil of the breaker.
Remote tripping of breaker – In this case, trip coil is connected (through wire) with panel which is installed at some other location. Tripping is done by remote push buttons.
- Types of LT Circuit Breakers –Following types of LT circuit breakers (Low Tension) are used in electrical system. These LT circuit breakers are used for up to 450V electrical supply.
- ACB (Air Circuit Breaker),
- MCCB ( Molded Case Circuit Breakers,
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breakers),
- ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker)
- RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breakers),
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Electrical Circuit Breakers –
Q1) How do electrical circuit breakers prevent electrical fires?
Ans) Electrical circuit breakers (ELCB/RCCB, MCB, MCCB, ACB, VCB) are of various types depending on the type of protection e.g. some circuit breakers provide protection against earth fault only while some protects against overcurrent (overloading & short circuit). The fault in electrical circuit due to overcurrent can cause fire in electrical system because when current exceeds its rated capacity then heating starts in equipment, cable, cable terminals due to I2R losses. If higher current will flow continuously in circuit then all these electrical items starts burning & this fire may spread in other parts of the building.
Therefore, it is very important that over current (more than rated capacity) in electrical system should be avoided. This can be done with circuit breakers. Circuit breakers in electrical system should be designed carefully so that breakers trip on fault. If breaker rating will be too high from the rated cable & equipment then it’s a problem. In this case breaker will not trip on higher current & other electrical items like cable & equipment will start burning. Similarly, if breaker current rating is low as compared with associated cable & equipment then on overcurrent fault beaker will trip again & again & disturb the supply frequently to the load.
Q2) How to determine ampere rating of circuit breakers in electrical panel?
Ans) Breaker current rating is decided according to full load current of the equipment. For example, if full load current of an equipment is 100A, then breaker rating should be at least 20-25% higher i.e. 125A. In breakers different -different current settings are available (specially in higher circuit breaker ratings such as MCCB & ACBs). Setting of the load can be done from 50% -110% depending on the requirement.
Q3) What is the difference between isolator & electrical circuit breakers?
Ans) Isolator is a device that is used to switch on / off electrical supply while circuit breaker is a device that is used to switch on / off and to protect electrical system form faults such as earth leakage, over loading and short circuit.
