Voltage
What is Electric Voltage – Definition of electric voltage is given below –
Definition –
The amount of potential energy between two points in a circuit. Where one point has more charge than another so the difference in charges between two points is called Voltage. It is measured in Volts. It is denoted by letter V.(Note: – Voltage is an electrical force which makes current to flow in a material.)
TYPES OF ELECTRIC VOLATGE–
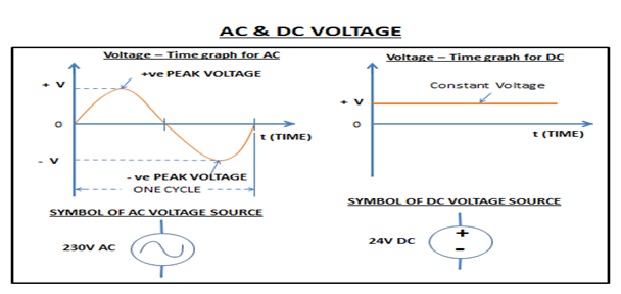
There are two types of voltage – AC Voltage & DC Voltage
AC Voltage –
It varies with respect to time & forms sinusoidal waves. AC voltage periodically reverses its direction.
Source of AC voltage –
a) Alternator – An alternator is a machine which coupled with some external rotating source & this source is turbine which may be operated from any one of the sources – steam which is produced through thermal power plant or atomic power plant, water fall which is received from Hydro Power plant,by Diesel or Gas engines, by wind power,
b) Converting DC voltage into AC voltage.
DC Voltage –
DC voltage doesn’t vary with time so it is represented by a straight line.
Source–Batteries, solar Cells, converting AC voltage into DC voltage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Electric Voltage–
Q1) What is the relation between electric power, current & voltage?
Ans) Voltage, current & power are closely linked with other which makes the electrical system to work. Let’s understand each one.
Voltage (V) –
It is a potential energy or potential difference between two points where one point has higher energy & other point has less. This voltage or potential difference provides a force to move the free electrons (negative charges) in a circuit/material. Voltage is denoted by letter V.
Current (I) –
Current is a rate at which charge flows. It is represented by the negative charge (or electrons) or in other words we can say that when electrons flows in a circuit, we can say that current is flowing in the circuit. Current is denoted by letter I.
Voltage & current –
Now what is the requirement of voltage & current? The purpose of voltage & current is to perform certain task. This task we generally call it load or electrical load. This electrical load may be a bulb, fan etc. Each load works on a certain voltage & current. If we apply a particular voltage to an electrical load, some current flows in the circuit/wire, passes through the load & load will work i.e. it will produce light in case of bulb or blade will rotate in case of fan.
Power (P) –
When this voltage & current combines for a load to work, this combination (V & I) becomes the power of the load or in other words we can say that this much power is required by the load to work. Or in other words we can say that Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The unit of power is the watt.
There are two types of power in electrical AC & DC. Bothe AC & DC are different in nature from each other (can be seen in the diagram given above), but AC power is widely used in day to day life (for domestic, commercial & industrial purpose).
Power in DC system –
P = V * I
Power in AC system –
Further, AC power is divided into Single phase power & Three phase power-
P = V * I * CosØ (where CosØ is power factor in AC system) – Single phase power
P = Г3 * V * I * CosØ (where CosØ is power factor in AC system)- Three phase power
Q2) What voltage an electric fence have?
Ans) Let’s understand the components of electric fence, it consist of three major components –
a) Fence wire, b) Energizer c) Earthing system
a) Fence wire –
Fence wire (preferably made of galvanized material due to anti rust) is a boundary which doesn’t allow unauthorized person/ animals to enter the premises. But, the normal fence could be broken by unauthorized persons/ animals. Therefore, some sort of protection is required to keep them away or doesn’t allow them to play with the boundary.
b) Energizer –
It a devise that produces a brief & high voltage pulses. This Energizer is connected with the fence wire, it sends a high voltage pulse for a fraction of seconds on regular intervals through the fence & other end of energizer is connected with ground. When any animal touches the fence, it gets electric shock because animal is standing on ground that complete the loop/circuit. This shock is the deterrent to the animal & not harmful. But animal moves away from the fence when it get electric shock. After few shocks from the fence, animals would avoid to come in contact with the fence.
The energizer are available in different forms – it may be battery operated, solar power powered & direct supply.
c) Grounding System –
Earthing / grounding system is also an important part of the system in which metal rods 3 nos are installed in the ground in triangle shape (approx. 3 metres away from each other) . The common point of these rods are connected with the energizer. This earthing system completes the current path from energizer to fence to animal & return back to energizer through the ground.
Q3) What is the voltage that is used for electric fence?
Ans) An energizer produces voltage in KVs. As a thumb rule the voltage in summer should not be less than 2000V while it should be more than 4000V in winter due to thick hair so that proper grounding could be achieved through the animal.
Q3) How to check voltage of electric fence with multimeter?
Ans) Multimeters are available to check the fence voltage. Use the multimeter which can show voltage in thousands (in kV) because fence volage is in thousands. First of all, set the knob of the multimeter in kV (thousand Volt) then touch the positive prob of it with the fence whose voltage is to be measured. Then ground the other prob with nearby metal surface, the meter will show/display the voltage of the fence.
Q4) Most electric dryers & ranges operate on what voltage?
Ans) In India most of the electric dryer operate on 220V, 50 Hz, single phase AC supply.
Q5) How much voltage does an electric eel has?
Ans) The Eel fish produces voltage in mV (mili-volt) in its cells. But when it senses danger, all these cell voltages combined together & reach up to 500V which is very dangerous for its enemy.
Q6) What is the voltage of an electric car battery? Or What voltage is needed to charge an electric car?
Ans) The battery of EVs is charged through DC supply. Now this DC voltage can be provided directly by DC supply or by converting AC supply into DC. That is why two types of EV chargers are available in market – DC Chargers & AC Chargers.
DC chargers are normally used for fast charging while AC Chargers are called slow chargers. In other words, we can say that slow charges take more time to charge the EV battery as compared the fast chargers.
Now, let’s talk about the DC voltage which needs for charging –
Two wheelers EV – 24V, 36V, 48V, 60 V
Three wheelers EV – 48V to 60 V
Four wheelers EV – 72V or higher
Q7) What causes of an electric shock – Current or voltage?
Ans) A person gets electric shock when current passes through his body. The amount of current decides the seriousness of the shock. The amount of current that flows in the body depends on voltage which has been touched & resistance of human body. The resistance of a human body is almost fixed (but it varies person to person which depends on the skin of a person), so current is directly proportional to the voltage. If voltage is high, more current will flow & vice versa.
(Note- The resistance of body may reduce if skin of a person is wet or damp either through sweating or water etc.)
Q8) What happens in the body when a person gets electric shock?
Ans) When a person gets electric shock & current passes through the body, that person may suffer from muscular contractions, failure of respiratory system, irregular heartbeat & burn injuries. Any one of them may become fatal but probability of fatality is more when current flows across the chest. And this situation arises when current flows either from one arm to another arm or one arm to opposite leg.
Q9) What is the safe working voltage?
Ans) Any voltage less than 50V is considered as a safe voltage.
Q10) What is normal electric home voltage? Or Electric voltage in India?
Ans) Electric home voltage is different in different countries. The value of voltage depends on the distribution system of that country. Normally, single phase AC supply is used for domestic or home purpose where 3 wire system is used (1- phase wire, 1- neural wire & 1 -earth wire). Some examples are given below –
- India – 230V AC, 50 Hz
- UK – 230V AC, 50 Hz
- US – 120V AC, 60 Hz
- China – 220V, 50 Hz
- Australia – 220V, 50 Hz
- Canada – 120V, 60 Hz
(Note- The above voltages are standard voltage, but these voltages may slightly vary when we will measure through voltmeter).
Q11) What is train electric voltage?
Ans) India – Electric train (Electric Traction) in India uses overhead line AC system which is 25KV, single phase, 50 Hz AC. This power is provided by State Electricity Board (SEB) through their electricity network of the state such as 220V/132V/110V/66V to Traction Sub Station (TSS). This high voltage is stepped down to 25V. These TSS are installed at a distance of 60 – 80 Km.
USA – In USA, traction system operates on 25KV, 60Hz AC.
Q12) Explain why an electric power is transmitted at high voltage?
Ans) Electrical power is transmitted at high voltage is due to reduce the losses. These losses occur due to current flow in the wires. Losses will be less, if current value is less & vice versa.
Lets’ understand like this from the formula of power (P = V * I, where V is inversely proportional to I) hence, we can say that for same amount of power, if voltage increases, the current will decrease.
Q13) What is the difference between EMF & Voltage?
Ans) Full form of EMF is Electro Motive Force which is the energy that is used to transfer a unit of electric charge in an electric circuit. This Emf can be produced by batteries, generators etc. (The electric charge may be positive (or protons) or negative (electrons) which is a physical property of matter.)
While Voltage is the potential difference which is the amount of energy utilized by a unit of electric charge. Voltage is measured across two terminals. In other words, we can say that emf generated by source /cell when reaches up to terminals becomes potential difference (or voltage) & its value reduces due to potential drop across the cell/source due to internal resistance. Both Emf & Voltage have same SI unit, Volt.
Difference between Emf & Voltage could be explained by following equations –
Emf is, E = I * (R + r)
While Voltage, V = I * R
where I = Current, R = Resistance of load & r = internal resistance of source/Cell.